Deborah R. Fowler
Linux Quick Guide
Updated on April 22 2016
Updated on Nov 15 2025
You can use command line to assemble your frames!
ffmpeg (see section on ffmpeg)
Visual Studio code (NOT Visual Studios) is code on both linux and Windows
Sublime is subl on linux(rocky) and sublime_text.exe on Windows
NOTE: You can use evince on linux to open a pdf via command line
NOTE: You can use eog on linux to open an image file via command line (it stands for Eye Of Gnome)
NOTE: You can use unzip on linux to extract files from dropbox.com
If you do not have access to linux and are on windows: Comparison of DOS versus linux commands.
NOTE: On windows you can use doskey to map things, such as doskey ls = dir
A note about forward / and backward \ slash in programming context
On Windows you can work in the cmd window and also the Powershell to get more of a linux like experience.
For example, on linux you create directory using mkdir, same in Windows. However something like printenv to print your path in linux becomes echo %Path%.
This would be redirected to a file. echo %Path% > test.txt
For more information about Windows see my MS-DOSHelpSheet
| Linux Quick
Guide |
to most
commonly used commands |
cmd on Windows |
| ls |
lists the contents of the directory (folders
are blue, files are black font) MS-Dos uses dir - on a whim, I tried this on linux and it works too! |
dir |
| cd |
change directory ie. cd ../
will go up a level or you may want to do to your home directory cd ~ or cd |
cd |
| ~ |
home directory |
|
| cp |
copy and if it is an entire directory, cp
-r (copy on msdos with no arguments) |
copy |
| cp -r |
entire directory | copy |
| copy on MS-Dos with no arguments will
copy folders intact xcopy src dest /s will copy all but not the top level (not very useful) |
||
| rm |
removes / deletes a file rm -r deletes
an entire directory |
del |
| pwd |
present working directory (where you are) |
echo %cd% |
| . |
current directory |
|
| ./ |
current directory |
|
| ps |
processor status (ie. what jobs are running) |
|
| kill -9 jobid |
kill the job with this id from ps no matter
what kill -segv will force it to save a version to /tmp |
|
| mkdir |
make a directory (new folder) |
mkdir |
| cd /opt |
installations of Houdini can be found here |
cd
C:/Program Files |
| & |
run an application as a background process gedit & this will leave the terminal window free to use |
notepad++.exe
& |
| keyboard up arrow |
recalls the last command to save typing or
... |
|
| history |
history lists recent commands and you can
type !# where # is the number from the list |
doskey /history F7 |
| and less
common but useful commands |
||
| printenv |
prints your
paths and environment settings |
echo %Path% |
| more |
pipes a file
to terminal display |
more |
| eog |
default image file viewer on linux (Eye of
Gnome) |
|
| evince |
evince file.pdf allow you to view a pdf file
via command line |
|
| unzip |
uncompress a zip file |
|
| whereis |
find where an application is located (and on Windows) where /r C:\ mplay.exe | where |
| On a mac use which |
Redirecting output
An easy thing to do on linux (or msdos) is to use a redirect output. So for example
python --version > test.txt
would create a file test.txt and put the output into that file
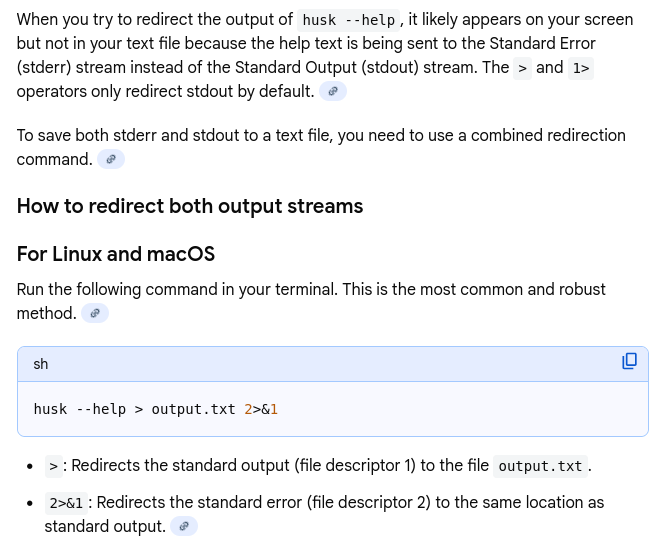
Not very useful for the above command, however something like husk it would be useful. If you try husk --help > test.txt your file will be empty - why?
The reason is the output from --help is going to Standard Error (stderr), not Standard Output (stdout)
To resolve this use
husk --help > test.txt 2>&1
How did I know this 2>&1? I didn't - I googled it - this works on msdos as well - try it (I've tested it using the hcmd or "command line tools" window from sidefx laucher). It is simply a cmd window with the Houdini env initialized.
Geany settings on linux (see also mix-fix)
- To change the terminal window size in geany
- xterm -fa "Mono:size=36" -e "/bin/sh %c"
- on Rocky no need to change, CentOS xterm
becomes gnome-terminal
Customizing with .bashrc
There are so many things you can do in linux from the command line!
You can create a .bashrc (used to be .custom_bash) script to be run when you log in.
The top of the .bashrc will have the line #!/bin/bash
This indicated that the file is a bash script and does not require any file extension, and /bin/bash is the location of the bash interpreter. (if it was Bourne shell /bin/sh)
A website with some simple examples of bash scripts can be found here
I would strongly advise you to use at least one line in there:
alias rm='rm -i'
That way it will query you when you delete a file.
Type in alias -h to see more options.
To run a script on our system, type ./name in a terminal, or double click on it in Nautilus (beware you must actually be in the directory or it will fail)
lifewire.com has some useful linux summaries, in particular for beginners here
Houdini Command Line rendering